This standard is an amendment to ZB J62 006.2-87 "Noise Limit Value for Open-Type Press Noise Limits of Forging Machine Noise Limits". This standard and the technical content of ZB J62 006.2-87 are basically the same, only according to the relevant provisions of the re-editing.
This standard has been implemented since January 1, 2000.
This standard replaces ZB J62 006.2-87 from the date of implementation.
Appendix A of this standard is an appendix to the standard.
This standard was proposed and managed by the National Standardization Technical Committee of Forging Machinery.
This standard is drafted by: Jinan Foundry Forging Machinery Research Institute.
This standard was first released in April 1987.
1 Scope This standard specifies the noise limits for sound pressure levels and sound pressure levels for open presses.
This standard applies to open fixed station presses and open-type tilting presses (hereinafter referred to as presses).
2 Reference Standards The following standards contain provisions that, through reference in this standard, constitute provisions of this standard. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards will be revised and all parties using this standard should explore the possibility of using the latest version of the following standards.
JB/T 3623-1984 forging machinery noise measurement method
3 Noise limits 3.1 The noise-weighted sound power level LWA of the press during continuous operation shall not be greater than that specified in Table 1. 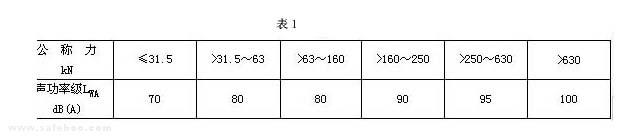
3.2 The noise level A sound pressure level LpA at the prescribed position of the press during continuous operation shall not be greater than that specified in Table 2.
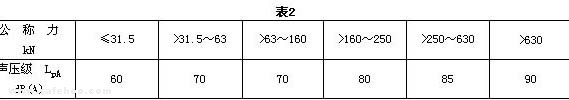
3.3 The impulse noise A-weighted sound pressure level LpA1 at a specified position during a single stroke of a no-load press shall not be greater than that specified in Table 3. 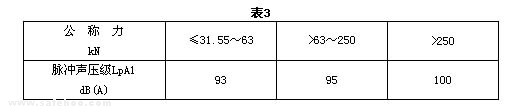
4 Measurement methods
The measurement method of this standard shall be in accordance with the provisions of JB/T 3623.
5 Instructions for use
The use of this standard is described in Appendix A (Appendix of the standard).
Appendix A
(standard appendix)
The instructions for the use of this standard A1 Any newly designed or improved prototype of a prototype, a new batch of trial-produced new products, or the first batch of press products produced after the process or material is changed, and presses for quality rating and performance testing The sound pressure level of the noise should be determined. It is recommended to determine the sound power level of the noise.
A2 Normal mass production presses can only measure the noise sound pressure level at the factory inspection.
Hoisting Mechanism And Spare Parts
The hoisting mechanism for a Tower Crane typically consists of a combination of a motor, a gearbox, wire ropes, and a hook block. Here is a breakdown of its components and how they work together:
1. Motor: The hoisting motor provides the power needed to lift and lower loads. It is usually an electric motor that generates high torque to handle heavy loads.
2. Gearbox: The motor's rotational motion is transmitted to the hoisting drum through a gearbox. The gearbox helps increase the torque and reduce the speed of the motor, enabling the crane to lift heavy loads at a controlled speed.
3. Hoisting Drum: The hoisting drum is a cylindrical drum around which the wire ropes are wound. It is directly connected to the gearbox and rotates as the motor operates. The drum's size and design determine the amount of Wire Rope it can hold.
4. Wire Ropes:
The wire ropes are wound around the hoisting drum and connected to the hook block. These ropes are made of high-strength steel and have a high load-bearing capacity. Multiple wire ropes are used to distribute the load evenly and ensure stability during lifting operations.
5. Hook Block: The hook block is attached to the lower end of the wire ropes and is responsible for carrying the load. It consists of a pulley system with one or more sheaves, which allows the wire ropes to change direction and support the load securely.
During operation, the motor drives the hoisting drum through the gearbox. As the drum rotates, the wire ropes are wound or unwound, depending on the direction of rotation. This movement raises or lowers the hook block, allowing the crane to lift or lower loads.
The hoisting mechanism is controlled by the crane operator using various controls and switches. Safety features such as limit switches and overload protection systems are also incorporated to prevent accidents and ensure safe lifting operations.
Hoisting Mechanism,Tower Crane Lift Motor,Tower Crane Axial Fans,Tower Crane Hoist Motor, Tower Crane Hoisting Reducer
SHEN YANG BAOQUAN BUSINESS CO., LTD , https://www.syconstructionhoist.com